What Is Schema Markup, Types & How To Implement It
In a world where every ranking matters, it’s easy to get lost. But there’s a tool that can help your website stand out – schema markup. Think of schema markup as a translator for search engines. It helps them understand your content better so they can show it to the right people. But many websites […]

In a world where every ranking matters, it’s easy to get lost. But there’s a tool that can help your website stand out – schema markup.
Think of schema markup as a translator for search engines. It helps them understand your content better so they can show it to the right people. But many websites are still missing out on its power.
In this guide, we’ll talk about what schema markup is, why it’s important for your SEO, and how to use it. Get ready to improve your website’s search engine ranking.

What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a type of microdata that you can add to your website’s HTML to improve how search engines read and represent your page in SERPs. It provides additional context to your content. This enables search engines to understand the specifics of your information more accurately.
Schema.org is a collaborative initiative by Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex. It provides a standardised vocabulary for structuring data. By using this vocabulary, you can ensure that your markup is compatible across different search engines.
Key Points:
- Contextual Understanding: Schema markup helps search engines comprehend the content and context of your pages.
- Enhanced Descriptions: It allows for creating rich snippets—detailed search results that include additional information like ratings, prices, or event dates.
- Improved Visibility: Enhanced search results can lead to higher click-through rates (CTR), even if your website doesn’t rank first.
Applying schema markup to a recipe page can enable search engines to display cooking time, ingredients, and user ratings directly in the search results. This makes your listing more attractive to users.
Why is Schema Markup Important?
Schema markup doesn’t just help search engines understand your content; it also boosts your website’s visibility in search results. This can drive more traffic and improve user interaction.
Benefits of Schema Markup:
-
Enhanced Visibility:
- Rich Snippets: Schema markup enables rich snippets, which display additional information like reviews, ratings, or event details. These snippets stand out in SERPs, attracting more attention from users.
- Knowledge Graph Integration: Properly marked-up content can be featured in the Knowledge Graph, appearing as information boxes on the side of search results.
-
Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR):
Even if your website isn’t at the top of the search rankings, rich snippets can draw users’ eyes, increasing the likelihood of clicks. Studies have shown that websites implementing schema markup can achieve up to four positions higher in SERPs than those without it.
-
Better SERP Presence:
Schema markup allows your website to appear in various rich results formats, such as carousels, rich cards, and enhanced listings, providing more opportunities for visibility.
-
Competitive Advantage:
Despite its benefits, less than one-third of websites apply schema markup. By adopting it, you position your website ahead of many competitors who haven’t yet embraced this technique.
-
Improved Ranking Potential:
While schema markup itself isn’t a direct ranking factor, the enhanced user experience and increased CTR can indirectly contribute to better rankings.
Statistical Insight:
- Websites with schema markup stand on an average of four positions higher in the SERPs than those without schema markup.
- One-third of search results on Google consolidate rich snippets, which incorporate schema markup.
- Less than one-third of websites apply schema markup, leaving a vast opportunity for improvement.
- Approximately a million websites are missing out on an enormous source of SEO potential by not utilising schema markup.
- According to Searchmetrics, about 36.6% of search keywords bring up at least one featured snippet that’s derived from schema markup.
These statistics underscore the tangible benefits of integrating schema markup into your SEO strategy. This highlights both its effectiveness and the significant opportunity it presents.
Types of Schema Markup
Schema markup isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. There are various types of schema markup, each designed to cater to specific content types and purposes. Implementing the appropriate schema type can enhance how your content is displayed in search results.
-
Product Markup
Ideal for e-commerce websites, product markup allows you to display essential product details such as price, availability and reviews directly in SERPs. This information helps potential customers make informed decisions and can increase the likelihood of clicks.
Example: Displaying a product’s price, star rating, and availability status beneath the search result.
-
Review Markup
Review markup showcases user ratings and reviews for your products or services. This builds trust with potential customers by providing social proof directly in search results.
Example: Displaying a 4.5-star rating based on user reviews for a restaurant or service provider.
-
Article Markup
For publishers, bloggers, and news websites, article markup is crucial. It helps your content appear in Google’s “Top Stories” and includes information like the author, publication date, and headline, enhancing your content’s visibility.
Example: Highlighting the author’s name, publication date, and a featured image for a news article.
-
Course Markup
If you offer educational content or online courses, course markup can display details such as course descriptions, instructor information, and schedule dates. This makes your educational offerings more discoverable.
Example: Displaying the course title, description, instructor name, and schedule for an online programming course.
-
Organisation Markup
This type of markup is perfect for businesses and organisations. It includes key information like name, address, contact details, and social profiles, enhancing local SEO and making your organisation more accessible.
Example: Displaying a business’s name, address, phone number, and social media links in search results.
-
Local Business Markup
Tailored for local businesses, this markup type improves local SEO by showcasing relevant business information such as location, opening hours, and customer reviews. It also enhances visibility in local searches and on Google Maps.
Example: Showing a local café’s address, hours of operation, and customer ratings in local search results.
-
FAQ Schema Markup
FAQ schema allows you to mark up frequently asked questions and their answers. This enables your content to appear in the rich FAQ format in search results. This can improve your SERP presence and provide users with quick answers.
Example: Displaying a list of frequently asked questions and answers for a software product in search results.
-
Video Schema Markup
For websites featuring video content, video schema markup can enhance how videos appear in search results by displaying thumbnails, descriptions, and duration. This can increase click-through rates and user engagement.
Example: Displaying a video thumbnail, description, and length for a tutorial video in search results.
Where Does Structured Data Appear in SERPs?
Structured data, implemented through schema markup, enhances your presence in several areas of the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). Understanding where and how it appears can help you strategise effectively.
-
Rich Snippets:
These extended search results include additional information like star ratings, prices, or event dates.
Rich snippets make your listing more informative and visually appealing, increasing the chances of user clicks.
Example: A product listing showing its price, availability, and customer ratings.
-
Knowledge Graph:
A knowledge graph provides information about entities (people, places, things) that appear in a dedicated information box, often on the right side of the SERP.
This enhances brand authority and provides users with quick access to key information.
Example: A company’s Knowledge Graph displaying its logo, contact information, and key services.
-
Rich Cards:
These are visual results displayed in a carousel format, particularly for specific content types like recipes or movies.
This increases visual appeal and interactivity, encouraging user engagement.
Example: A carousel of recipe cards showing images, cooking times, and ratings.
-
Featured Snippets:
Featured Snippets are a summary of an answer to a user’s query that appears at the top of the SER and is extracted from a webpage.
It positions your content as an authority on the topic, often leading to increased traffic.
Example: A concise answer to a “How-to” question, along with relevant steps or tips.
-
Breadcrumbs:
This displays the page’s location within the site hierarchy, making it easier for users to navigate.
It enhances user experience by providing clear navigation paths.
Example: Showing “Home > Blog > SEO > Schema Markup” beneath the page title.
Understanding these placements helps you optimise your schema markup to maximise visibility and user engagement across different sections of the SERP.
How to Implement Schema Markup on Your Website (Step by Step)
Implementing schema markup can seem daunting, especially if you’re new to SEO. However, with the right tools and a systematic approach, you can integrate schema into your website with ease.
Step 1: Identify the Content to Mark Up
Before diving into coding, determine which parts of your website would benefit most from schema markup. Common candidates include:
- Products: For eCommerce sites.
- Articles: For blogs and news sites.
- Events: For event listings.
- Local Businesses: For local SEO.
- FAQs: For informational content.
Step 2: Use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
Google offers a user-friendly tool to assist in generating schema markup.
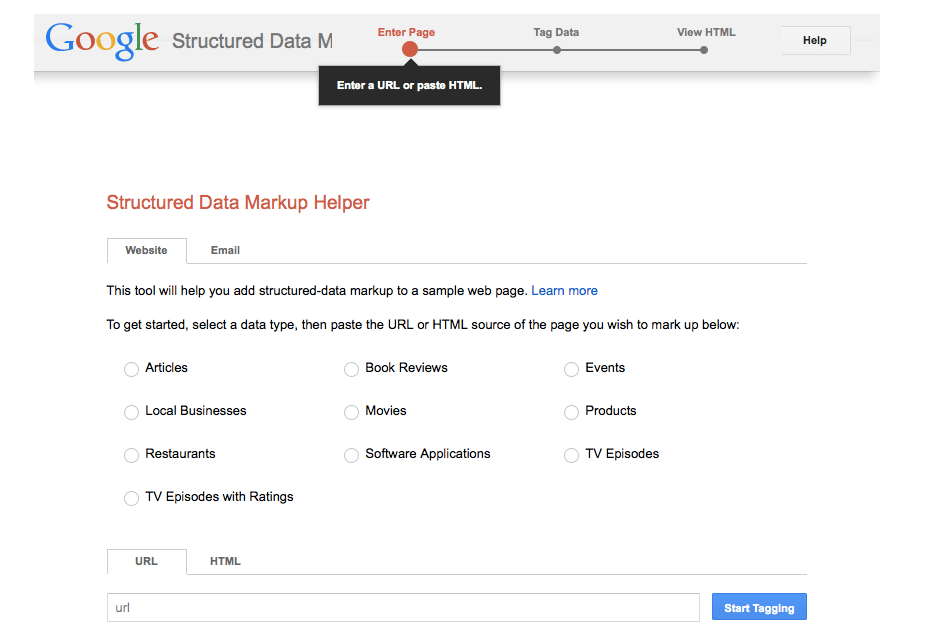
-
Access the Tool:
Navigate to [Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper]
-
Select Content-Type:
Choose the type of content you want to mark up (e.g., Article, Local Business, Product).
-
Input Your Content:
Enter the URL of the page you wish to mark up or paste the HTML code directly.
-
Tag the Data:
Highlight and select the appropriate tags for different elements on your page (e.g., title, author, image).
-
Generate HTML:
After tagging, click “Create HTML” to generate the marked-up code.
Step 3: Add the Markup to Your Website
Once the markup is generated, integrate it into your website’s HTML.
-
Manual Integration:
If you’re comfortable editing HTML, paste the generated schema code into the appropriate sections of your webpage.
-
Using a Content Management System (CMS):
If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, consider using plugins to simplify the process (discussed in the next step).
Step 4: Automate Schema Markup with a Plugin
For those using CMS platforms, plugins can streamline the schema markup process.
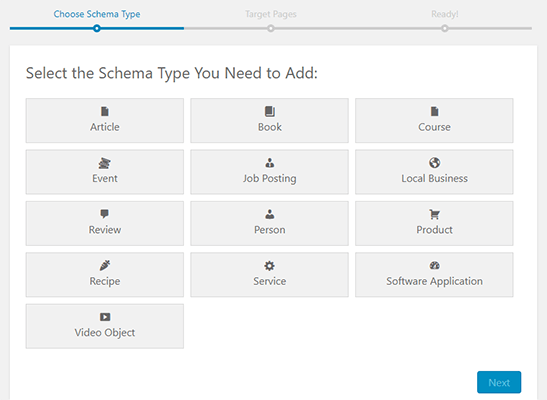
-
Choose a Plugin:
Popular options include Yoast SEO, All in One Schema Rich Snippets, and Schema Pro.
-
Install and Activate:
Install the chosen plugin from your CMS’s plugin repository and activate it.
-
Configure Settings:
Follow the plugin’s setup instructions to configure schema types and fields.
-
Apply Schema to Content:
Use the plugin’s interface to add schema markup to your posts, pages, or products without manual coding.
Step 5: Validate Your Markup
After implementing schema markup, it’s crucial to ensure it’s error-free.
-
Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool:
- Visit the Structured Data Testing Tool and input your URL or paste the code.
- Review the results to identify and fix any errors or warnings.
-
Use Rich Results Test:
- The Rich Results Test tool helps verify if your markup is eligible for rich results.
-
Monitor with Google Search Console:
- After validation, monitor your schema markup performance and any issues via Google Search Console.
Step 6: Monitor and Update
SEO is an ongoing process. Regularly monitor your schema markup’s performance and update it as needed to align with any changes in your content or schema.org updates.
How to Validate Your Schema Markup
Ensuring your schema markup is correctly implemented is vital for it to function as intended. Validation helps identify and rectify errors that could prevent search engines from recognising your markup.
Tools for Validation:
-
Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool:
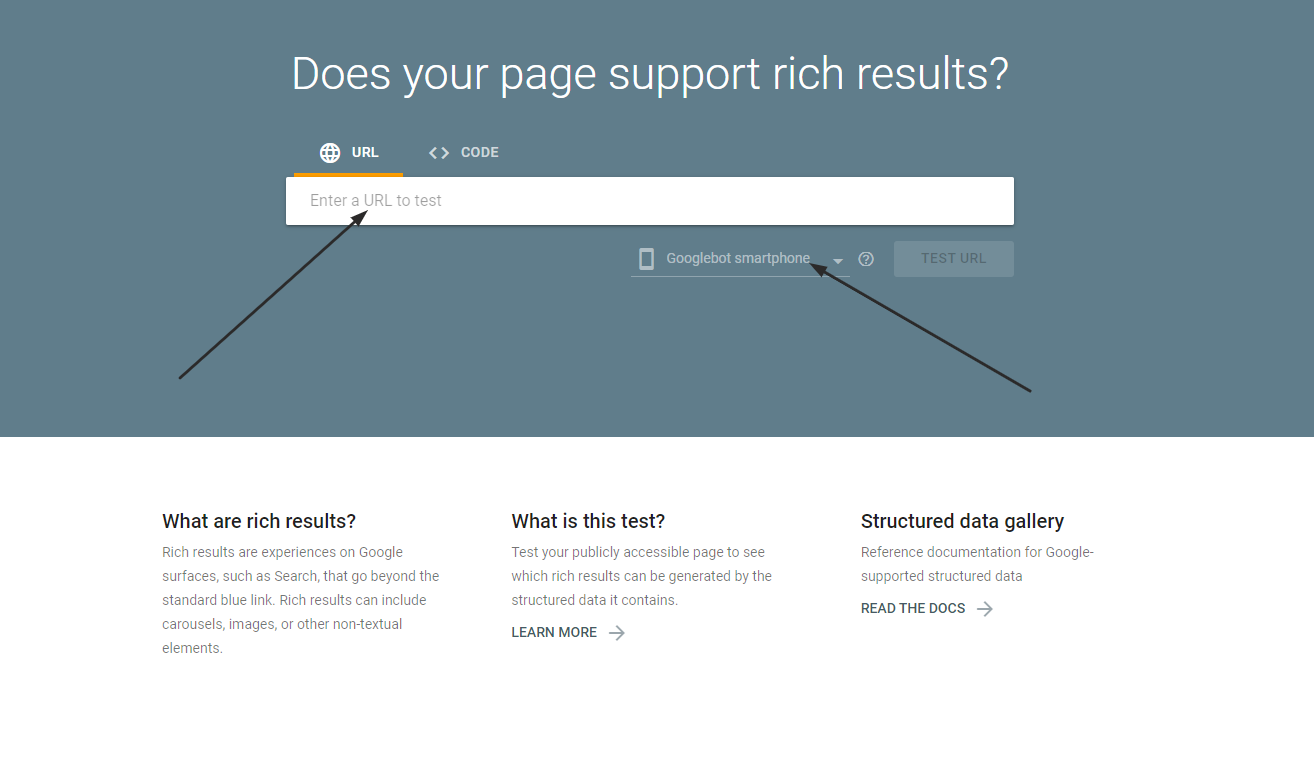
- Usage: Paste your code or enter your page URL to check for proper implementation.
- Features: Identifies errors and warnings and provides a preview of how your rich snippets will appear.
-
Rich Results Test:
- Usage: Enter the URL or code snippet to test whether your page is eligible for rich results.
- Features: Provides detailed insights into which rich result types your page supports.
-
Schema Markup Validator:
- Usage: A community-driven tool to ensure your schema is error-free and compliant.
- Features: Supports the latest schema.org updates and offers comprehensive validation.
Best Practices for Validation:
- Regular Checks: Periodically validate your schema markup, especially after making changes to your website.
- Fix Errors Promptly: Address any errors or warnings identified during validation to maintain optimal performance.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of updates to schema.org and adjust your markup accordingly to leverage new features and types.
Schema Markup Best Practices
To maximise the benefits of schema markup, it’s essential to follow best practices that ensure its effectiveness and compliance with search engine guidelines.
-
Use Specific Schema Types
Always opt for the most relevant schema type for your content. Using specific types enhances the accuracy and usefulness of your rich snippets.
Example: Use Recipe schema for a cooking blog instead of the generic Article schema.
-
Ensure Accuracy and Consistency
Provide accurate and up-to-date information in your schema markup. Inconsistencies between your markup and actual content can lead to penalties or reduced trust from search engines.
-
Avoid Over-Optimisation
While schema markup is beneficial, avoid marking up every single element on your page. Focus on the most important aspects that add value to the user experience.
-
Follow Google’s Guidelines
Adhere to Google’s Structured Data Guidelines to ensure your markup is compliant and eligible for rich results.
-
Regularly Update Your Schema
As your content evolves, update your schema markup to reflect any changes. This ensures ongoing relevance and accuracy in search results.
-
Monitor Performance
Use tools like Google Search Console to track the performance of your schema markup. Analyse metrics such as CTR and impressions to gauge effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
-
Leverage JSON-LD Format
Google recommends using JSON-LD to add schema markup as it’s easier to implement and maintain than other formats like Microdata.
Example:
“`json
“`
-
Provide Comprehensive Information
Include as much relevant information as possible within your schema markup to enhance the richness of your snippets.
Example: For a product, include price, availability, brand, and review ratings.
Conclusion
Schema markup is not just a fleeting trend in the SEO world. It’s a foundational element that enhances how search engines interpret and display your content. By providing structured data, you enable search engines to present your website in more informative and visually appealing ways, thereby increasing your chances of attracting clicks and engaging users.
What's Your Reaction?





































.png)